
Since the 1850s gold rush era in California, mining operators have relied on a backfilling process to refill excavated areas created during underground mining. This process is essential for maintaining mine stability, ensuring a safe working environment, and reducing the environmental impact at the end of the mine’s lifecycle.
In this article, we explore the most common backfill technologies used in mining, including Rockfill, Hydraulic Backfill, and Paste Backfill. We will also discuss key valve types and design features for paste backfill applications, emphasizing options that minimize maintenance and reduce downtime.
Backfill Technology Options
Backfill technologies play a crucial role in underground mining, offering solutions that enhance stability, safety, and efficiency. Below, we will explore the most common methods used by mining operators: Rockfill, Hydraulic Backfill, and Paste Backfill.
Rockfill
Rockfill is a backfill technique that involves blending crushed rock, often sourced directly from the mine, with a cement slurry to create a durable, concrete-like material. The crushed rock is carefully prepared by sizing and sieving before being mixed with the slurry. This blending process can take place either at the surface or within underground facilities. Once ready, the mixture is transported to the mine stopes, where it is either poured or compacted into place.
This method is relatively simple and cost-effective, with lower initial investment and technical complexity compared to other backfill options. However, maintaining consistent material quality can be challenging, and the mixture often requires a significant curing period, ranging from 3 to 21 days, before it solidifies. While material costs remain low due to a binder content of just 4-6%, operational costs can rise due to factors like truck maintenance, fuel, labor, and ventilation for underground transport.
Hydraulic Backfill
Hydraulic backfill relies on water to transport materials such as coarse tailings, slag, and sand, combined with binders like cement or fly ash. After the finer particles are removed from the tailings, the materials are mixed at the surface and transported underground through pipes and boreholes using gravity. Bulkheads are installed to hold the backfill in place while excess water is drained. The drainage rate significantly impacts the curing period, and influences backfill scheduling and mining operations.
Although the process itself is relatively simple, it requires precise control over material composition to achieve the desired strength and efficient drainage. If water drainage is too slow, it can compromise bulkhead stability, lead to voids in the fill, or necessitate additional applications to address issues. The humid conditions created by dewatering can also cause wear on underground equipment and vehicles.
Typically, hydraulic backfill systems operate under low pressure, but deeper mine sections may require systems capable of handling pressures as high as 80 to 100 bar with binder content ranging from 0–15%, while curing times can extend from 7 to 28 days. Overall, hydraulic backfill requires a relatively low initial investment, but careful planning and maintenance are critical to ensure efficiency and reliability.

Paste Backfill
Paste backfill is a method that transforms thickened tailings from the mine’s milling process into a dense material by mixing them with cement, and occasionally aggregates, to enhance strength. This backfill material is then delivered to underground stopes via pipelines, either through pumping or gravity-fed systems.
With a lower water content than hydraulic backfill, paste backfill eliminates the need for dewatering, significantly reuses mine waste, and offers faster curing times. The binder content is relatively low, typically between 3–6%, helping to control material costs.
However, paste backfill systems involve higher upfront costs due to the sophisticated equipment required to produce a consistent and durable mix. Operating costs are also elevated because the high pressures in distribution systems—ranging from 30 to 60 bar and potentially reaching up to 130 bar—can lead to increased wear and the risk of pipe blockages. Additionally, this method requires a high level of technical expertise to ensure the backfill meets strength and quality standards. Despite these complexities, paste backfill efficiency in recycling waste and reducing cycle times makes it a valuable choice for mining operations.
Knife Gate Valves
To ensure worker safety and maintain continuous mining operations, it is essential to minimize disruptions caused by valve maintenance or replacement. Armour Valve distributes, CMO Knife Gate Valves in Canada, including the standout XB series. Known for its cost-effectiveness, excellent chemical compatibility and durability, the XB is the valve of choice for tailings operators around the world. The XB series is a bidirectional lug type polyurethane coated knife gate valve offering high flow rates with low/medium pressure drops.
Additional valve features that help extend service life in paste plants include:
Corrosion Resistance: Its poly-lined construction ensures exceptional protection against corrosion, making it an ideal solution for handling corrosive materials. This durability reduces maintenance costs and downtime while extending the valve’s service life.
Smooth Operation: The poly lining minimizes friction and wear, providing seamless operation while reducing energy consumption and improving overall performance.
Leak-Proof Design: The knife gate mechanism delivers a tight shut-off, effectively preventing leaks and maintaining process integrity, which helps minimize material loss.
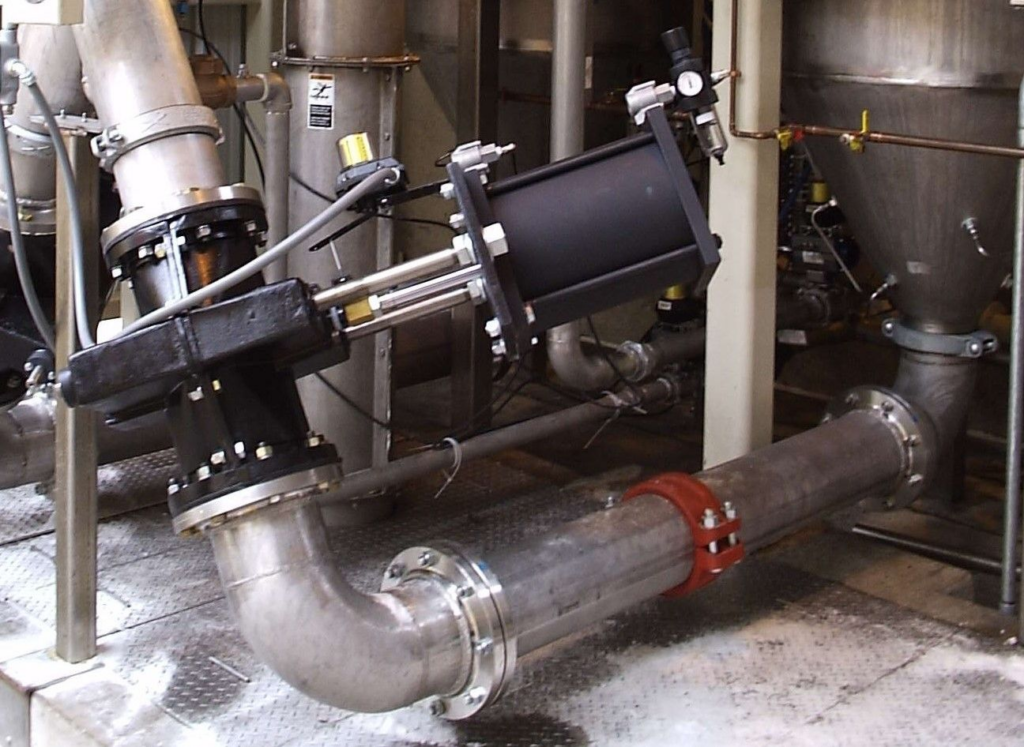
Source: Onyx Valves
Pinch Valves
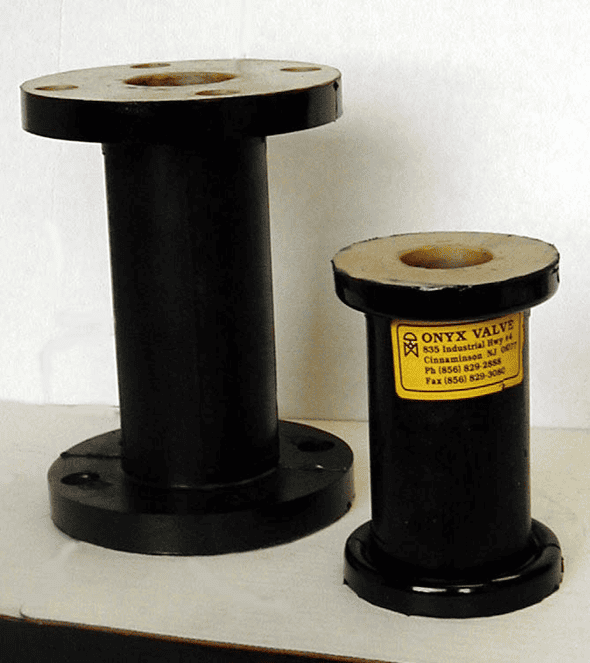

Onyx Valve Compression Molded Sleeve
When it’s necessary to regulate flow and fine-tune slurry consistency at the inlet of a mixing tank, pinch valves are often the preferred solution. These valves control flow by compressing an elastomer sleeve inside a housing using one or two movable bars. While they can be costly in larger sizes, pinch valves are known for their clog-resistant design and the added benefit of not requiring stem packing.
The elastomer sleeve is the core component of a pinch valve. Some manufacturers craft these sleeves using a heat tape process on a mandrel, followed by vulcanization.
Onyx Valve utilizes a more advanced approach that places the sleeve into a compression mold before vulcanization. This method results in improved dimensional accuracy and a stronger bond between the rubber and fabric, ensuring superior performance and durability.
O-Port Slide Gate Valves
Ball valves, while robust, are prone to issues in paste applications due to the significant dead space between the inlet flange and the seat/ball sealing area. This dead space increases the likelihood of material solidifying, which can lead to operational disruptions if the paste plant experiences downtime. O-port slide gate valves offer a practical solution to minimize these challenges.
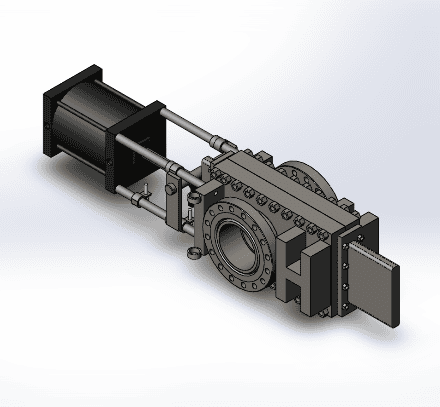
Stainless Valve Co. O-port Slide Gate Valves
Proven for use in low-pressure pulp and slurry operations, as well as high-temperature and abrasive environments, O-port slide gate valves are now designed to handle high-pressure applications. In mining paste plants, their compact lug-body design significantly reduces dead space, mitigating the risk of material buildup.
To ensure reliability, these valves feature glass-filled PTFE guides in the upper and lower stuffing boxes for precise blade alignment, while PTFE seats deliver consistent, drip-tight sealing. Actuation can be achieved using pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders, making them a dependable choice for demanding paste handling operations. Armour Valve distributes Stainless Valve Co. O-port slide gate valves that reduce dead space and are suitable for the higher pressure paste plant service.
Let’s Help You Find the Right Valve Solution
At Armour Valve, we understand the critical role valve solutions play in mining operations. Whether for paste backfill applications, slurry systems, or auxiliary services, we provide reliable, high-performance products designed to optimize efficiency, minimize maintenance, and ensure operational success.
Let us help you enhance your mining operations with the right valve solutions. Contact Armour Valve today to discuss your needs and explore how we can support your project requirements.

